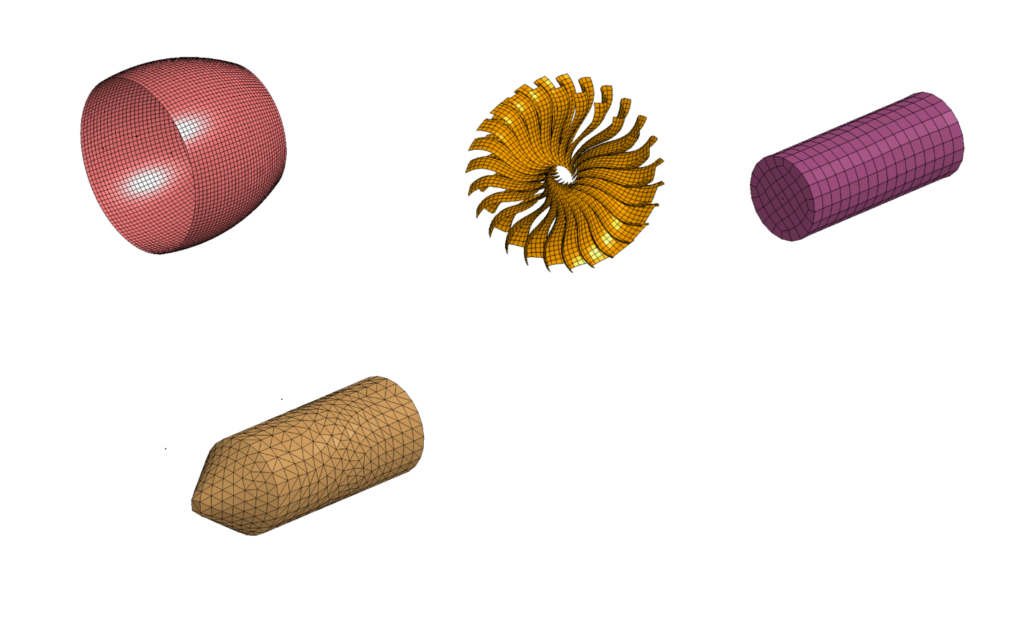
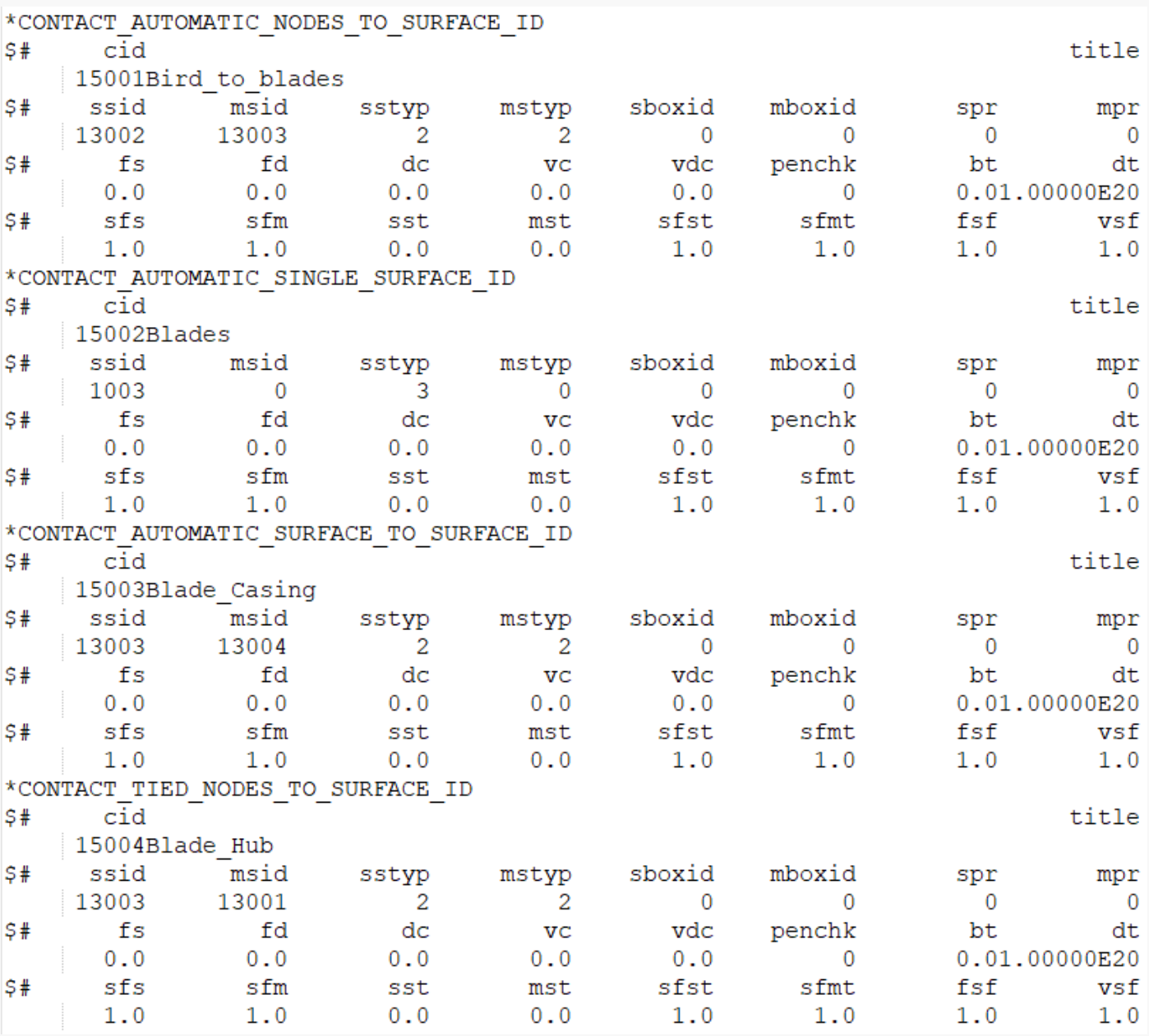
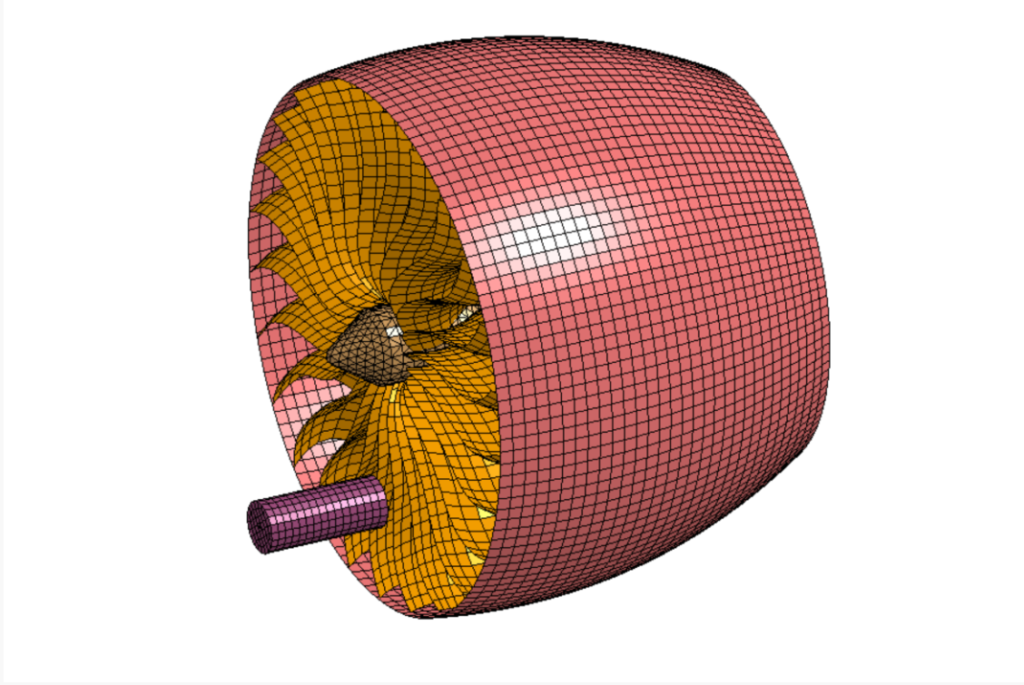
A classic non-linear transient dynamics problem, the bird strike problem was solved using a generic explicit solver in LS-Dyna. While accurate modeling of the problems requires advanced techniques such as Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics, the aim here was to understand the nuances such as consistent numbering approach, contact-modeling, control card setup, and usage of multiple input files akin to industry model setup in LS-PrePost. The model consisted of 4 components: blades, hub, bird, and casing. The unit system of this model is kg-mm-ms. Aluminum-titanium alloy has been used as a material for blades, steel is used for the casing and the hub, and properties akin to human muscle have been used for the bird object. General Single surface, node-to-surface, and surface-to-surface contacts have been used. A mass-Scaling of 3.2% has been used to study its impact on the simulation time. Finally, all the cards and simulation controls have been called to a main input file to execute the problem.